
CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates are the body primary source of energy. It is commonly known as “Carbs”. It is of the three
Macronutrient, essential for human diet, alongside proteins and fats. It is made up of chains of sugar
molecules. Carbohydrates contains about 4 calorie/gram.
45% to 65% of carbs should be come from your diet. Atleast, 125 grams of carbs is essential for living. For
daily gym goers, carbs intake should be 6 to 10 gram/kilogram of your Bodyweight daily.
Further, Carbs are classified into two categories:-
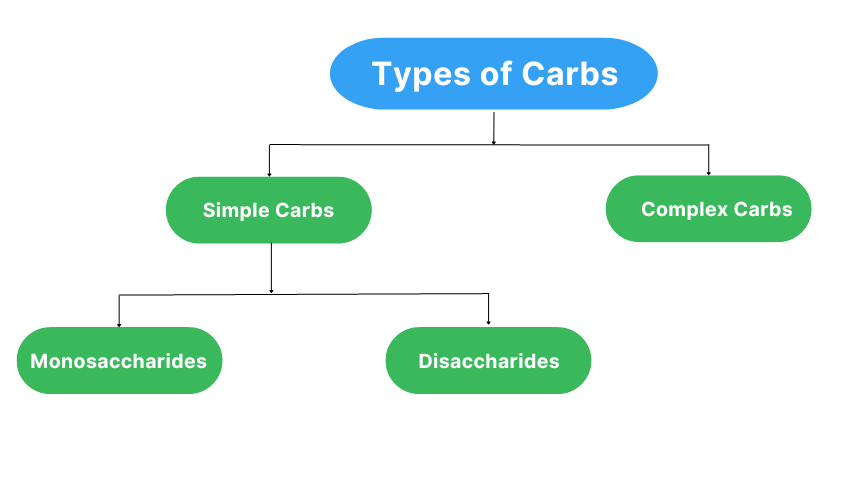
- Simple carbs include sugars (monosaccharides)
- sugars combined with glucose (disaccharides).
Monosaccharides is the simplest form of sugar. It three types:-
- Glucose is midly sweetener
- Fructose is very sweetener
- Galactose is hardly sweet
Carbs in the diet are broken down into glucose through digestion. This glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream, where it becomes readily available for cells to use as an energy source. The process of glucose metabolism occurs through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. This intricate series of reactions produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells.
Fructose is a natural sugar found in many fruits, vegetables, and honey. It is a monosaccharide, meaning it is a simple sugar that cannot be broken down into smaller sugars. They are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. While fructose is naturally occurring in various foods, it is also commonly used as a sweetener in processed foods and beverages.
Examples- Fructose is naturally present in significant amounts in fruits such as apples, pears, grapes, and bananas. It is also found in vegetables like tomatoes, beets, and sweet potatoes. Honey is another rich source of fructose.
Galactose is a monosaccharide, a type of simple sugar that is crucial for various biological processes. They are not usually found alone in nature but is often present in combination with glucose to form lactose. They are found in smaller amounts in fruits, vegetables, and some grains.
Disaccharides is the form of sugar which has two monosaccharides. It three types:-
- Maltose
- Sucrose
- Lactose
Maltose is composed of two glucose molecules linked together. It is commonly referred to as malt sugar because it is produced during the germination of grains, especially barley, as a result of the enzymatic breakdown of starch.
Sucrose is composed of two simple sugar molecules i.e, glucose and fructose. It is commonly known as table sugar. Sucrose is often used as a sweetener in a variety of foods and beverages, and it plays a key role in human nutrition as a source of energy. When you consume sucrose, enzymes in your digestive system break it down into its constituent sugars, glucose, and fructose, which can then be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body for energy. It is naturally found in many plants, particularly in sugarcane and sugar beets, from which it is commonly extracted for commercial use.
Lactose is a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Lactose is the primary carbohydrate in the milk of mammals, including humans. Lactose is unique in that it requires the enzyme lactase for proper digestion in the human body. Lactase breaks down lactose into its constituent sugars, allowing for absorption in the small intestine.
Complex carbs are long chains of sugar molecules. Also, known as “Polysaccharides”. It includes glycogen , starch and fiber.
- Glycogen
- Starch
- Fiber
It is found in small quantities in meat and not at all in plants. It is not a significant food source of carbs but has an important role in the storage of glucose in the liver and muscles.
It is found in grains, legumes, and tubers(root vegetables) . Plant stores of glucose which are composed of 100s and 1000s of glucose molecules. These can be fully digested and are hydrolyzed to glucose for the body's energy needs.
The structural part of plants which is found in all plant foods i.e grains, fruits and vegetables. Also, includes cellulose, pectin and gums. Fiber cannot be broken down by the digestive system and therefore does not contribute to the body's glucose stores, but it has an important role in digestion and health.
Carbs consumed that are not immediately used are stored as glycogen. Glycogen is stored in the liver and muscle cells and can be broken down to provide rapid energy, especially for high intensity movement. The amount of glycogen we can store can be increased by training but remains limited to a maximum of about 2,000 calories in muscles and 300 in the liver. Also, glycogen is large and bulky because of containing large amount of water molecules.
The role of carbs in Athletic performance may be better determined by its GI. The body transforms carbs into blood glucose at different rates an indicater of the speed of relative rise in blood glucose is called the GI. The GI is a measure that ranks carb containing foods based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and cause a quick spike in blood sugar, while those with a low GI are digested more slowly, resulting in a gradual and sustained release of glucose. It is important to know that that the GI applies only eaten alone. If eaten as part of a complex meal, these change in complex and unpredictable ways. So, it is in fact difficult to classify “good” or “bad”. It changes the glycemic index. For those who do daily resistance training, if your workout sessions exceed over 1hr, they should consume 30 to 60 g/hr of carbs to maintain blood glucose level. This is particularly important in extreme Heat, Cold and High altitudes. Examples of carbs source- Sports drinks, Energy bars and Carbohydrate powders. After exercise, you should intake 1.5 g/kg of your Bodyweight in the first 30 minutes. And repeat this in every 2hrs for next 4 to 6 hrs.